How to choose your destination
Copy linkDepending on your preference, choosing a destination involves many criteria with different priorities. Below are some common criteria to consider when making your decision.
University
Ranking
The Global Pathways program partners with top-ranked universities, most of which are in the top 1% worldwide. Some are part of Australia’s research-intensive Group of Eight (Go8). Students can be confident in the educational quality and should consider other criteria.
Here are some renowned university rankings for your reference:
– QS World University Rankings
– THE World University Rankings
– Maclean’s Education Ranking
Transfer Requirements
After gaining admission to ISB, students need to meet the transfer requirements to start their studies overseas. Adapting to a foreign learning environment can be challenging, so it’s advisable to aim for academic performance that exceeds the transfer requirements.
Expense
When calculating the expenses associated with studying abroad, it is crucial to take into account several factors. These include tuition fees, potential scholarships, and the cost of living in the area of the chosen university.
Location
Each location offers unique experiences. Students may consider factors such as the climate and weather, the surrounding communities, and the post-study work policies.
Climate and weather
Considering the climate and weather for a destination can enhance comfort, health, and enrich experiences in line with personal and academic goals. You may find necessary information from the following links:
– Australia: Weather in Australia
– New Zealand: New Zealand climate and weather
– Canada: Weather, climate and hazards
Surrounding communities
The local community is another factor in students’ decision-making process when choosing a study destination. For example, in New South Wales, students have a variety of options. They could choose Macquarie University, located in the Macquarie Park Innovation District, known for its numerous start-up companies. Alternatively, they could opt for the University of Technology Sydney, which is situated right in the Sydney Central Business District. For those who prefer a more serene community, the University of Wollongong in Wollongong Beach City would be a considerable choice.
Post-study work policy
Many countries offer policies for international students seeking work opportunities after graduation. These policies aim to facilitate real-world application of their studies and gain international work experience. Here are the government websites providing post-study work policies:
– Australia: Temporary Graduate Visa – Post-Study Work Stream, Designated Regional Areas
– New Zealand: Post-Study Work Visa
– Canada: Post-Graduation Work Permit
Support
Each partner university offers both general and specialised support for students. General support is available to almost all students, while specialised support caters to students from specific fields of study, degrees, or majors. More information about these services can be found on the university websites and faculty pages.
Degree and Major
Most universities provide a course finder or student handbook on their websites. These resources offer information about degrees and majors, including course overviews, course structures, career outcomes, etc. Students can explore their preferred degrees and majors using the following links:
– Curtin University, Australia: Curtin Course Finder
– Deakin University, Australia: Deakin Course Finder
– Griffith University, Australia: Study at Griffith
– Macquarie University, Australia: Macquarie Course Finder
– Monash University, Australia: Monash Course Finder
– The University of Adelaide, Australia: Adelaide Degree Finder
– The University of Queensland, Australia: Queensland Program Finder
– University of South Australia, Australia: Study at UniSA
– University of Tasmania, Australia: UTas Course Finder
– University of Technology Sydney, Australia: UTS Course Finder
– The University of Western Australia, Australia: Find a course at UWA
– University of Wollongong, Australia: Study at UOW
– Western Sydney University, Australia: WSU Program Finder
– Massey University, New Zealand: Massey Course Finder
– The University of Waikato, New Zealand: Waikato Course Finder
– Dalhousie University, Canada: Dalhousie Academics
– University of New Brunswick, Canada: UNB Academic Programs Search
Transfer Model
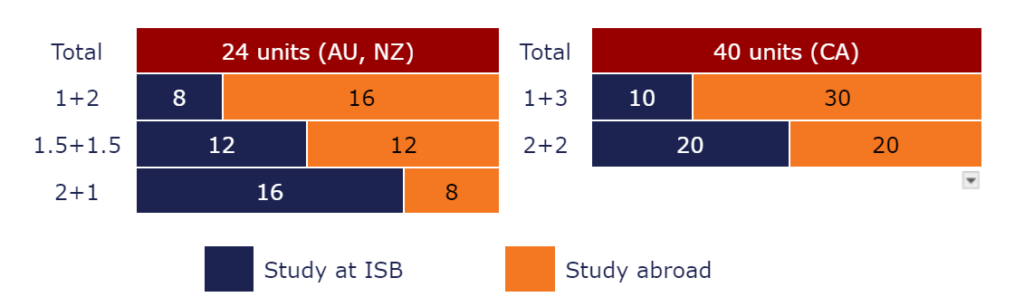
A Bachelor’s degree usually requires about 24 units over 3 years in Australia and New Zealand, and around 40 units over 4 years in Canada. The transfer model you choose determines the division of units between studying at ISB and studying abroad, with options varying by university, degree, and major.
Each transfer model has unique advantages. For instance, the 1+2 model, which includes a year in Vietnam followed by two years abroad, allows more time to adapt to studying in English and university-level skills under the instructions of qualified ISB lecturers. This initial stage in Vietnam facilitates smoother transition to a foreign institution, as evidenced by the high achievements of students who have transferred. In addition to academic and career goals, Global Pathways students can expand their network in both Vietnam and abroad. On the other hand, the 2+1 model includes the first two years in Vietnam and the final year abroad. It is a cost-effective model, however, it offers fewer degree and major choices than the 1+2 model and does not satisfy the requirements for a post-study work visa unless studies are extended.